The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires covered entities and business associates to protect sensitive patient data. Two critical components of HIPAA compliance are Risk Analysis and Risk Management. Performing these thoroughly ensures that healthcare organizations safeguard protected health information (PHI) and avoid costly fines and breaches.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a HIPAA Risk Analysis and implement Risk Management effectively.
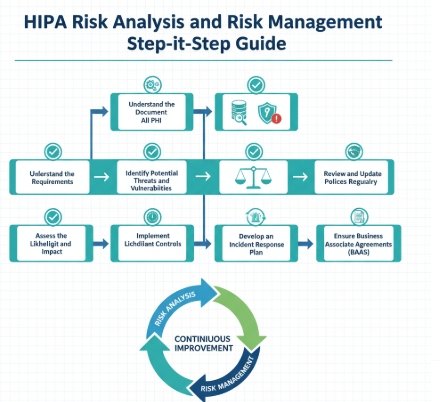
✅ Step 1 – Understand the Requirements
Start by familiarizing yourself with the HIPAA Security Rule and Privacy Rule. These set the standard for safeguarding PHI by requiring organizations to:
- Identify risks and vulnerabilities.
- Implement safeguards.
- Monitor and revise security measures.
✅ Step 2 – Identify and Document All PHI
Make a comprehensive list of where PHI is created, received, maintained, or transmitted. This includes:
- Electronic systems (EHRs, databases).
- Paper records.
- Portable devices like laptops, USB drives.
- Communication tools like emails or messaging apps.
Document the flow of data to understand how PHI moves within and outside your organization.
✅ Step 3 – Identify Potential Threats and Vulnerabilities
Look for areas where PHI might be at risk. Common threats include:
- Unauthorized access or data theft.
- Malware, ransomware attacks.
- Human error such as misplacing documents.
- System failures or technical glitches.
- Physical threats like theft or natural disasters.
Vulnerabilities might include outdated software, weak passwords, or insufficient employee training.
✅ Step 4 – Assess the Likelihood and Impact
For each identified threat, determine:
- Likelihood: How probable is it that this risk will occur?
- Impact: What would be the severity of damage if it happens?
Use a risk matrix to prioritize which issues need immediate attention.
✅ Step 5 – Implement Safeguards and Controls
Once risks are assessed, create an action plan to mitigate them:
- Install antivirus and firewalls.
- Encrypt data during storage and transmission.
- Restrict access based on roles.
- Provide employee training on HIPAA policies.
- Backup data regularly.
Document all safeguards and ensure they are aligned with HIPAA’s requirements.
✅ Step 6 – Review and Update Policies Regularly
Risk environments change over time. Regular audits and updates help ensure ongoing compliance:
- Conduct periodic risk assessments.
- Update security protocols when new technologies are implemented.
- Train staff on new threats and policies.
- Maintain documentation of audits, decisions, and corrective actions.
✅ Step 7 – Develop an Incident Response Plan
Prepare for potential breaches by:
- Defining who to contact in case of a security incident.
- Establishing procedures for reporting and investigating breaches.
- Notifying affected individuals as required by HIPAA rules.
Having a documented response plan minimizes damage and ensures accountability.
✅ Step 8 – Ensure Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
Work with third-party vendors that handle PHI and ensure they sign Business Associate Agreements. These agreements require vendors to comply with HIPAA rules and safeguard data appropriately.
Final Thoughts
Conducting HIPAA Risk Analysis and implementing Risk Management is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. By carefully identifying threats, assessing vulnerabilities, and applying appropriate safeguards, healthcare organizations can maintain trust, protect sensitive information, and avoid regulatory penalties.
If you have any queries or need more updates on HIPAA compliance, risk analysis, or management practices, just drop us an email, and we’ll be happy to assist you.